Unveiling the Principles of Ecology Worksheet Answers: Delving into the intricacies of ecological principles, this comprehensive resource provides a thorough understanding of the concepts that govern the interactions within ecosystems.
Through a meticulous exploration of key ecological principles, energy flow, nutrient cycling, ecosystem interactions, and human impacts, this guide equips readers with the knowledge necessary to navigate the complexities of ecological systems.
1. Key Ecological Principles: Principles Of Ecology Worksheet Answers

Ecological principles provide the foundation for understanding the intricate relationships between organisms and their environment. These principles guide the study of ecosystem dynamics, species interactions, and the impact of human activities on natural systems.
Carrying Capacity and Ecosystem Stability
Carrying capacity refers to the maximum population size that an ecosystem can support indefinitely without degrading its resources. It is determined by various factors such as food availability, water resources, shelter, and disease. Exceeding carrying capacity can lead to overpopulation, resource depletion, and environmental degradation.
Density-Dependent and Density-Independent Factors
Density-dependent factors are those that affect population growth based on population size. These include competition for resources, predation, and disease. Density-independent factors, on the other hand, affect population growth regardless of population size, such as natural disasters, climate change, and habitat destruction.
Competition, Predation, and Mutualism
Competition occurs when organisms compete for limited resources. Predation involves one organism (predator) consuming another (prey). Mutualism is a symbiotic relationship where both species benefit from the interaction. These interactions shape ecological communities by influencing species abundance, distribution, and evolutionary adaptations.
2. Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycling
Energy and nutrients are essential for life and must constantly flow through ecosystems. Understanding these processes is crucial for comprehending the functioning and productivity of natural systems.
Flow of Energy
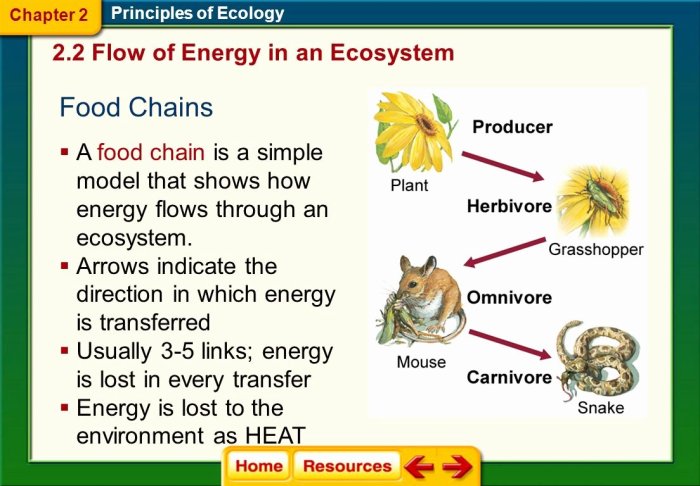
Energy enters ecosystems through producers (autotrophs) via photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. It is then transferred through consumers (heterotrophs) in a linear fashion, from primary consumers (herbivores) to secondary consumers (carnivores) and so on. At each trophic level, energy is lost as heat and only a small fraction is passed on to the next level.
Nutrient Cycling
Nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon, are essential for plant growth and ecosystem productivity. Decomposers (bacteria and fungi) play a vital role in nutrient recycling by breaking down dead organisms and returning nutrients to the soil or water.
Food Chains, Food Webs, and Trophic Levels, Principles of ecology worksheet answers
Food chains are linear representations of energy flow, while food webs depict the complex interconnected feeding relationships within an ecosystem. Trophic levels represent the position of organisms within the food web, from producers to top predators.
3. Ecosystem Interactions and Disturbances
Ecosystems are constantly subject to disturbances, both natural and human-induced. Understanding the impact of these disturbances is essential for managing and conserving ecosystems.
Types of Disturbances
Natural disturbances include hurricanes, fires, floods, and volcanic eruptions. Human-induced disturbances include pollution, habitat destruction, and climate change.
Impact of Disturbances
Disturbances can have both positive and negative effects on ecosystems. They can create new habitats, promote species diversity, and stimulate ecological succession. However, severe disturbances can also lead to species loss, ecosystem degradation, and disruption of ecological processes.
Ecological Succession
Ecological succession refers to the gradual change in species composition and ecosystem structure following a disturbance. Over time, disturbed ecosystems undergo a series of successional stages until they reach a relatively stable climax community.
4. Human Impacts on Ecosystems
Human activities have a profound impact on ecosystems worldwide. Understanding these impacts is critical for developing strategies to mitigate their negative effects and conserve natural systems.
Major Impacts
Major human impacts include habitat destruction, pollution, overexploitation of resources, and climate change. These activities can disrupt ecosystem processes, reduce biodiversity, and lead to environmental degradation.
Biodiversity and Ecosystem Stability
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms within an ecosystem. It is essential for ecosystem stability, resilience, and productivity. The loss of biodiversity can weaken ecosystems and make them more susceptible to disturbances.
Conservation Strategies
Conservation strategies aim to protect and restore ecosystems and mitigate human impacts. These strategies include habitat protection, species conservation, sustainable resource management, and pollution control.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is carrying capacity?
Carrying capacity refers to the maximum population size that an ecosystem can sustain indefinitely, considering the availability of resources.
How do density-dependent factors affect population growth?
Density-dependent factors, such as competition and predation, increase in intensity as population density rises, limiting population growth.
What is the role of decomposers in nutrient cycling?
Decomposers break down dead organisms and organic matter, releasing nutrients back into the ecosystem for reuse by producers.
How can human activities disrupt ecosystems?
Human activities, such as pollution, habitat destruction, and climate change, can alter or disrupt ecosystems, impacting their structure and function.