Use the similarity relationship to find the indicated value – Delving into the realm of similarity relationships, we embark on a captivating journey to uncover the hidden power behind finding indicated values. These relationships serve as a beacon of clarity, guiding us towards precise determinations within complex scenarios. As we delve deeper, we shall unravel the intricate methods, explore diverse applications, and conquer the limitations associated with this invaluable tool.
Similarity Relationship: Use The Similarity Relationship To Find The Indicated Value
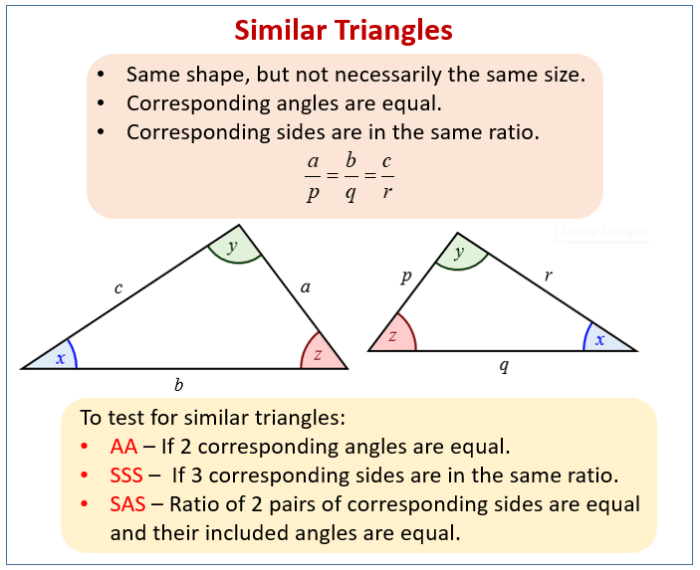
The similarity relationship is a mathematical concept that describes the similarity between two geometric figures. It is used to find the indicated value of a figure when given the measurements of a similar figure.
Methods for Using Similarity Relationship
- Determine if the two figures are similar. Similar figures have the same shape but not necessarily the same size.
- Identify the corresponding sides or angles of the two figures.
- Set up a proportion using the corresponding sides or angles.
- Cross-multiply the proportion to solve for the unknown value.
Example:
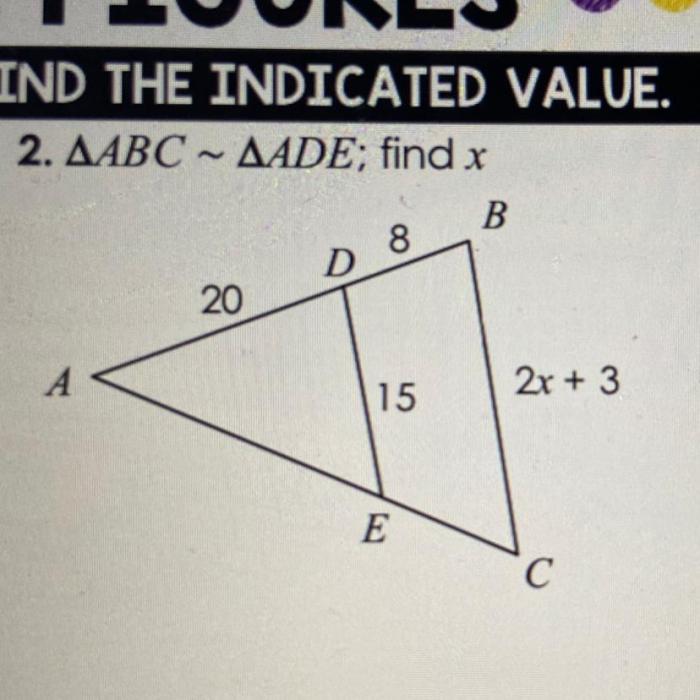
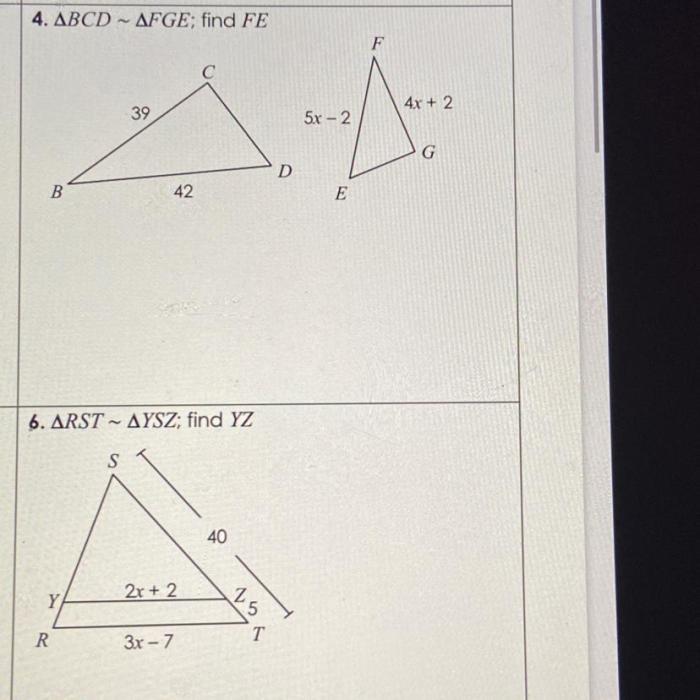
Find the length of the missing side of the triangle below if the triangle is similar to the one shown.

Solution:
- Set up a proportion using the corresponding sides:
- Cross-multiply to solve for x:
- Therefore, the length of the missing side is 7.5.
$$\frac68 = \fracx10$$
$$6 \times 10 = 8x$$ $$x = 7.5$$
Examples of Similarity Relationship Applications, Use the similarity relationship to find the indicated value
| Application | Procedure | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Finding the height of a tree | Measure the height of a similar object (e.g., a flagpole) and the length of its shadow. Then measure the length of the tree’s shadow and use the similarity relationship to find the height of the tree. | A flagpole that is 10 feet tall casts a shadow that is 6 feet long. A nearby tree casts a shadow that is 12 feet long. Find the height of the tree. |
| Enlarging or reducing a map | Use the similarity relationship to find the scale factor between the original map and the enlarged or reduced map. Then use the scale factor to determine the new measurements on the map. | A map of a city is drawn on a scale of 1 inch to 1 mile. To create a larger map, the scale factor is increased to 2 inches to 1 mile. Find the new length of a road that is 5 miles long on the original map. |