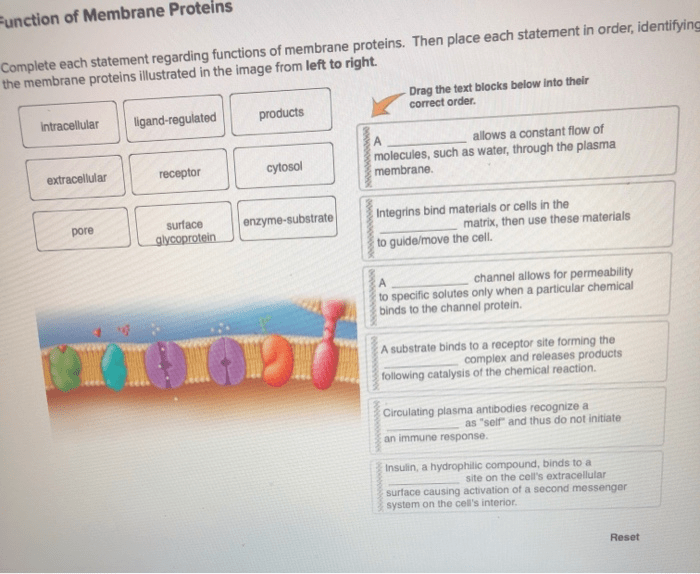
Complete each statement describing the functions of membrane proteins sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with academic style and authoritative tone and brimming with originality from the outset.
Membrane proteins, the gatekeepers of cells, orchestrate a symphony of functions that sustain life’s intricate dance. From facilitating communication to enabling nutrient exchange, these molecular marvels play a pivotal role in cellular processes. Join us on an exploration of their diverse functions, unraveling the secrets of these enigmatic proteins.
Functions of Membrane Proteins: Complete Each Statement Describing The Functions Of Membrane Proteins
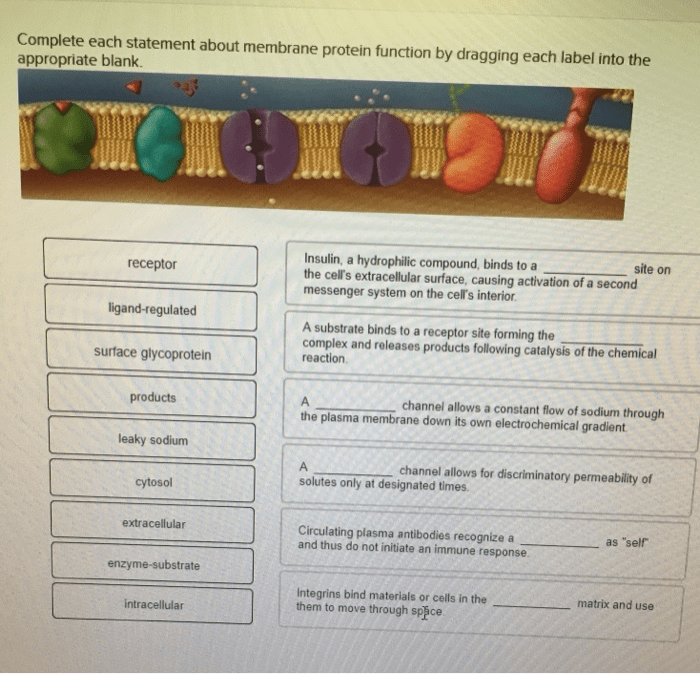
Membrane proteins are integral components of cell membranes that play crucial roles in various cellular processes. They are responsible for facilitating the movement of molecules across the membrane, cell signaling, and nutrient transport.
Types of Membrane Proteins and Their Structures
Membrane proteins can be classified into two main types based on their structure: integral membrane proteins and peripheral membrane proteins.
- Integral membrane proteinsare embedded within the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane. They have hydrophobic regions that interact with the lipid tails and hydrophilic regions that interact with the aqueous environment on either side of the membrane.
- Peripheral membrane proteinsare not embedded in the lipid bilayer. They are loosely attached to the membrane surface and interact with integral membrane proteins or the lipid head groups.
Role of Membrane Proteins in Cell Signaling
Membrane proteins play a critical role in cell signaling by facilitating communication between cells. They can bind to specific ligands or signaling molecules, triggering a cascade of events that lead to a cellular response.
- Ligand-gated ion channels: These membrane proteins open or close ion channels in response to the binding of a ligand, allowing the flow of ions across the membrane and triggering electrical signals.
- G protein-coupled receptors: These membrane proteins bind to ligands and activate G proteins, which in turn activate other signaling molecules to initiate a cellular response.
Functions of Membrane Proteins in Nutrient Transport, Complete each statement describing the functions of membrane proteins
Membrane proteins enable the movement of nutrients across cell membranes, ensuring that cells have access to the essential molecules they need for growth and function.
- Transporters: These membrane proteins bind to specific nutrients and facilitate their transport across the membrane by facilitated diffusion or active transport.
- Channels: These membrane proteins form pores that allow nutrients to pass through the membrane without the need for a carrier protein.
Table: Functions of Membrane Proteins
| Function | Type of Membrane Protein | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Cell signaling | Ligand-gated ion channels | Acetylcholine receptor |
| Cell signaling | G protein-coupled receptors | Adrenergic receptor |
| Nutrient transport | Transporters | Glucose transporter |
| Nutrient transport | Channels | Potassium channel |
Challenges in Studying Membrane Proteins
Studying membrane proteins presents several challenges due to their hydrophobic nature and complex structure.
- Isolation and purification: Membrane proteins are difficult to isolate and purify from cell membranes without denaturing them.
- Limited experimental techniques: Traditional experimental techniques such as X-ray crystallography and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy have limitations in studying membrane proteins due to their dynamic nature.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are membrane proteins?
Membrane proteins are proteins embedded in the lipid bilayer of cell membranes, enabling communication and transport across the membrane.
What are the different types of membrane proteins?
Membrane proteins are classified into two main types: integral membrane proteins, which span the entire membrane, and peripheral membrane proteins, which are loosely attached to the membrane surface.
What are the functions of membrane proteins?
Membrane proteins perform a wide range of functions, including cell signaling, nutrient transport, and regulation of cellular processes.