Embark on a linguistic journey with the Official Language of Pakistan Crossword, a captivating exploration of the history, significance, and usage of the language that unites a nation. From its historical roots to its contemporary challenges, this comprehensive guide unravels the complexities of Pakistan’s official language, revealing its profound impact on society, culture, and national identity.
Delve into the origins and evolution of the language, tracing its influences and the factors that shaped its adoption. Discover the regional variations and dialects that add a rich tapestry to the linguistic landscape of Pakistan. Explore the literary and artistic expressions that have flourished in this language, showcasing the works of renowned authors, poets, and artists.
Definition and Overview
The official language of Pakistan is Urdu, a standardized register of the Hindustani language. Urdu holds a significant historical and cultural position in the country, serving as a symbol of national identity and a medium of communication across diverse regions.
Historical Evolution
Urdu emerged in the 12th century as a fusion of Persian, Arabic, and local Prakrit dialects. During the Mughal Empire, it gained prominence as the court language and spread throughout the Indian subcontinent. After the partition of India in 1947, Urdu was adopted as the official language of Pakistan, reflecting its widespread use and cultural significance.
Socio-cultural Significance

National Identity
Urdu serves as a unifying force for Pakistanis, fostering a sense of national cohesion and belonging. It is the language of government, education, media, and literature, connecting people from different regions and backgrounds.
Communication, Official language of pakistan crossword
Urdu is the primary medium of communication in Pakistan, facilitating interactions between people from diverse linguistic and cultural groups. It plays a crucial role in fostering social cohesion and understanding.
Education
Urdu is the official language of instruction in primary and secondary education in Pakistan. It is also used in higher education institutions, particularly in the humanities and social sciences.
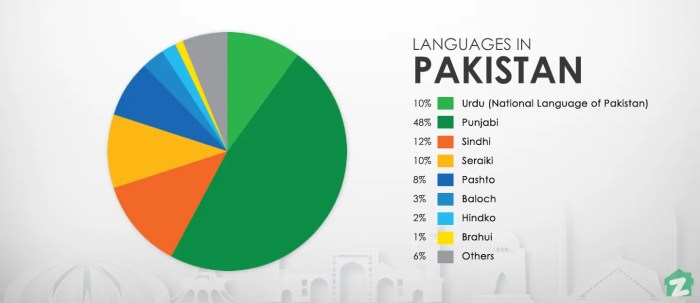
Regional Variations
While Urdu is the standard official language, there are numerous regional dialects and variations spoken in different parts of Pakistan. These dialects often incorporate local words and phrases, reflecting the cultural diversity of the country.
- Punjabi: Spoken in Punjab province, the most populous region of Pakistan.
- Sindhi: Spoken in Sindh province, known for its unique literary and cultural traditions.
- Balochi: Spoken in Balochistan province, characterized by its distinct vocabulary and grammar.
- Pashto: Spoken in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province, influenced by the neighboring Afghanistan.
Literary and Artistic Expression

Urdu has a rich literary tradition, producing notable poets, writers, and artists. It is the language of classic works such as Mirza Ghalib’s poetry and Saadat Hasan Manto’s short stories.
- Mirza Ghalib: A renowned Urdu poet known for his ghazals, exploring themes of love, loss, and spirituality.
- Saadat Hasan Manto: A celebrated short story writer, known for his unflinching portrayal of social issues and human nature.
- Faiz Ahmed Faiz: A progressive poet, whose work addressed themes of social justice and political freedom.
Modern Usage and Challenges: Official Language Of Pakistan Crossword
Urdu continues to be the official language of Pakistan, but its usage has evolved in recent times. English has gained prominence in education, business, and technology.
Challenges
- Preservation: Ensuring the preservation and promotion of Urdu in the face of globalization and the influence of English.
- Modernization: Adapting Urdu to meet the demands of modern society, including the development of technical and scientific terminology.
Opportunities
- Education: Promoting Urdu as a medium of instruction in higher education, particularly in technical and scientific fields.
- Technology: Leveraging technology to create online resources and tools for Urdu language learning and dissemination.
Cross-Cultural Perspectives
Urdu shares similarities with other official languages in the world, particularly those spoken in South Asia.
Similarities
- Hindi: Urdu and Hindi are closely related languages, sharing a common origin and grammatical structure.
- Bengali: Both Urdu and Bengali have been influenced by Persian and Arabic, and they share some vocabulary.
Differences
- Script: Urdu is written in the Perso-Arabic script, while Hindi is written in the Devanagari script.
- Vocabulary: Urdu incorporates more words from Persian and Arabic, while Hindi draws more from Sanskrit.
FAQ Guide
What is the official language of Pakistan?
Urdu
When was Urdu adopted as the official language of Pakistan?
1947
What are the major regional dialects of Urdu?
Lahori, Multani, Sindhi
Who are some notable Urdu authors?
Mirza Ghalib, Saadat Hasan Manto, Faiz Ahmed Faiz