Apwh unit 4 transoceanic interconnections – APWH Unit 4: Transoceanic Interconnections unveils the profound impact of maritime exploration and trade on global history. From the Silk Road to the Age of Exploration, transoceanic voyages transformed societies, fostered cultural exchange, and laid the groundwork for modern globalization.
Advancements in maritime technology, such as the compass and astrolabe, empowered explorers to venture into uncharted waters. These voyages not only expanded geographical knowledge but also facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and diseases, shaping the course of human civilization.
Transoceanic Voyages and Trade
Transoceanic voyages played a pivotal role in the development of global trade and cultural exchange. They enabled the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies across vast distances, connecting civilizations and fostering the spread of knowledge and culture.
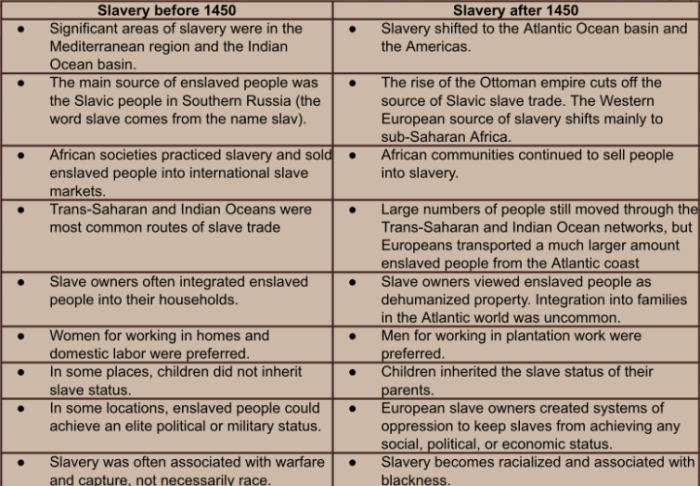
Major transoceanic trade routes included the Silk Road, the Indian Ocean trade network, and the trans-Atlantic slave trade. These routes facilitated the exchange of goods such as spices, textiles, precious metals, and slaves.
Impact of Transoceanic Voyages
- Spread of ideas: Transoceanic voyages facilitated the exchange of ideas, including religious beliefs, philosophical concepts, and scientific knowledge.
- Technological advancements: Voyages led to advancements in maritime technology, such as the development of the compass and the astrolabe, which improved navigation and exploration.
- Spread of diseases: Transoceanic voyages also facilitated the spread of diseases, such as smallpox and malaria, which had devastating effects on indigenous populations.
Maritime Technology and Exploration
Advancements in maritime technology were crucial for enabling transoceanic voyages. The development of ships with improved stability, speed, and capacity allowed explorers to venture further into the open seas.
Cartography and navigation also played a vital role. Maps and charts provided explorers with a better understanding of the world’s geography, while instruments like the astrolabe and compass aided in navigation.
Famous Explorers
- Christopher Columbus: Explored the Americas in the 15th century.
- Ferdinand Magellan: Led the first circumnavigation of the globe in the 16th century.
- James Cook: Explored the Pacific Ocean and Australia in the 18th century.
Cultural Encounters and Exchange
Transoceanic voyages led to significant cultural encounters and exchanges between different civilizations. These encounters had a profound impact on art, music, literature, and religion.
For example, the introduction of European art and music to the Americas influenced the development of new artistic styles and musical genres.
Specific Cultural Exchanges
- Columbian Exchange: The exchange of plants, animals, and diseases between the Americas and Europe following Columbus’s voyages.
- Spread of Buddhism: Transoceanic voyages facilitated the spread of Buddhism from India to China and Japan.
- Islamic Architecture: Islamic architecture influenced the design of buildings in many parts of the world, including the Americas.
Imperialism and Colonialism: Apwh Unit 4 Transoceanic Interconnections
Transoceanic voyages facilitated the expansion of European empires and the establishment of colonies around the world. European powers sought access to new resources, markets, and territories.
Motivations for imperialism included economic gain, political power, and religious zeal. Colonialism had significant consequences for indigenous populations, including displacement, exploitation, and cultural assimilation.
Specific Colonial Empires
- British Empire: The largest empire in history, with colonies in Africa, Asia, and the Americas.
- Spanish Empire: Controlled vast territories in the Americas and the Philippines.
- Portuguese Empire: Established colonies in Brazil, Africa, and Asia.
Global Connections and Interdependence
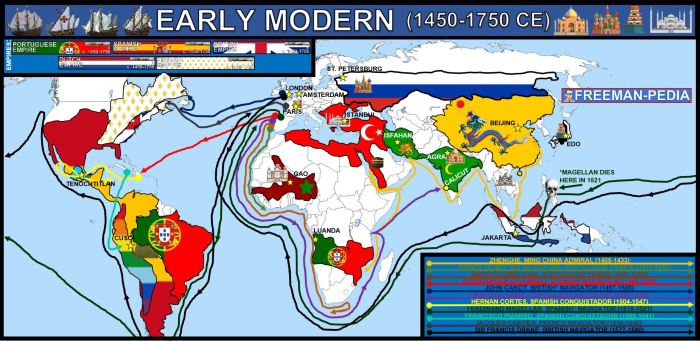
Transoceanic voyages contributed to the creation of a more interconnected and interdependent world. The exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies fostered economic, political, and social connections between different regions.
These connections have shaped the modern world, influencing everything from trade patterns to cultural diversity.
Examples of Global Connections, Apwh unit 4 transoceanic interconnections
- International trade: Transoceanic voyages enabled the global exchange of goods, leading to the development of international trade networks.
- Political alliances: Maritime trade and exploration fostered political alliances and cooperation between nations.
- Cultural diffusion: Transoceanic voyages facilitated the spread of cultural practices, beliefs, and languages across different continents.
Essential FAQs
What were the major transoceanic trade routes?
The Silk Road, the Indian Ocean trade network, and the Atlantic slave trade were among the most significant transoceanic trade routes.
How did transoceanic voyages contribute to the spread of diseases?
Explorers and traders carried diseases from one continent to another, leading to devastating pandemics such as the Black Death.
What were the motivations for European imperialism?
European imperialism was driven by a combination of economic, political, and religious factors, including the search for resources, markets, and converts.