In the competitive landscape of music streaming, a music website charges x dollars to access its vast library of songs. This pricing model has sparked discussions and debates, raising questions about its impact on user acquisition, revenue generation, and the overall music industry.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of pricing strategies for music websites, exploring different models, their advantages and disadvantages, and the factors that influence their effectiveness.
From flat-rate pricing to tiered pricing and usage-based models, this guide analyzes the implications of each approach, providing insights into their impact on user behavior, customer satisfaction, and revenue optimization. Additionally, it examines the role of value-added services, market segmentation, and competitive analysis in shaping the pricing strategies of music websites.
Subscription Models
Subscription models allow music websites to offer access to their content and services on a recurring basis. There are various subscription models that a music website can implement:
- Flat-rate subscription: Users pay a fixed monthly or annual fee for unlimited access to the entire music library.
- Tiered subscription: Users can choose from different subscription plans that offer varying levels of access and features, typically at different price points.
- Usage-based subscription: Users pay based on their usage, such as the number of songs streamed or the duration of listening time.
Advantages and Disadvantages
- Advantages for the music website:
- Provides a stable and recurring revenue stream.
- Encourages user loyalty and retention.
- Allows for targeted marketing and personalized recommendations.
- Advantages for users:
- Unlimited access to a wide range of music.
- Convenience and ease of use.
- Cost-effective compared to purchasing individual songs or albums.
- Disadvantages for the music website:
- High initial investment to acquire subscribers.
- Competition from other subscription services and free music streaming platforms.
- Potential for churn if users are not satisfied with the value offered.
- Disadvantages for users:
- Recurring monthly or annual cost.
- Limited access to music outside the subscription library.
- Data usage and storage requirements for streaming music.
Successful Subscription Models
- Spotify:Flat-rate subscription with tiered options for premium features.
- Apple Music:Flat-rate subscription with exclusive content and artist-curated playlists.
- Amazon Music Unlimited:Flat-rate subscription with access to Amazon’s extensive music catalog.
Pricing Strategies
Pricing strategies play a crucial role in attracting and retaining users. Music websites adopt different pricing models to optimize revenue generation and user satisfaction:
Flat-Rate Pricing
A fixed monthly or annual fee provides unlimited access to all content and features. This model is simple and easy to understand for users, but it may not be suitable for websites with a large music library or a high cost of acquiring new subscribers.
Tiered Pricing
Users can choose from multiple subscription plans with varying levels of access and features, typically at different price points. This model allows music websites to offer a range of options tailored to different user needs and budgets.
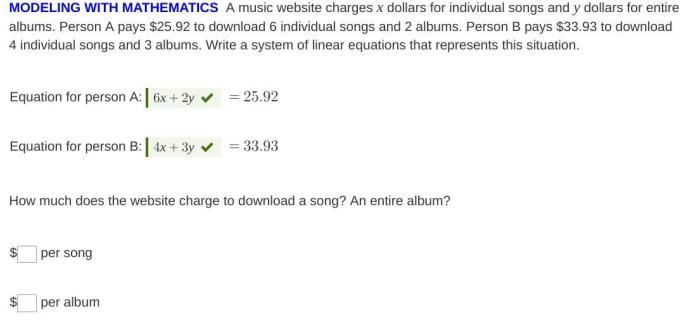
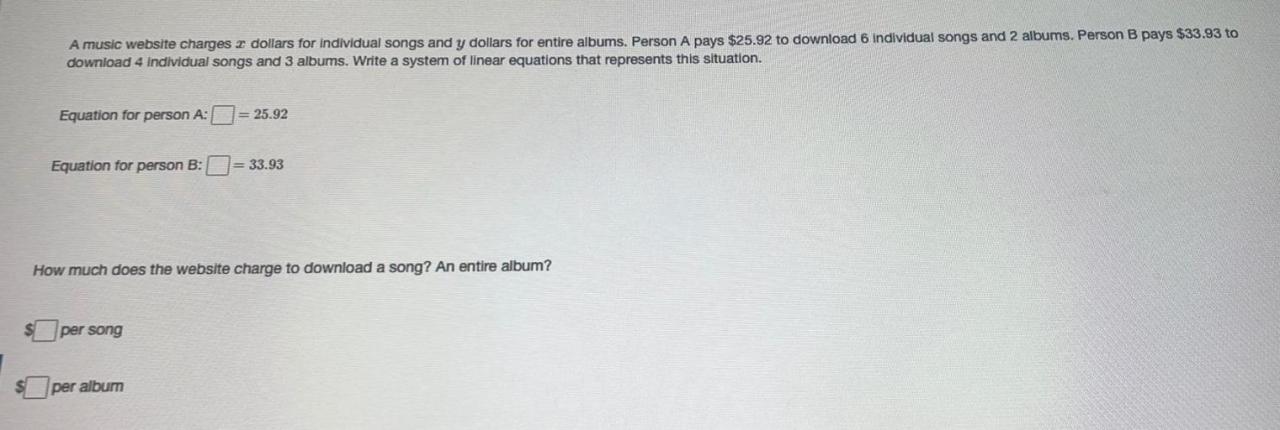
Usage-Based Pricing, A music website charges x dollars
Users pay based on their usage, such as the number of songs streamed or the duration of listening time. This model can be more cost-effective for users who do not listen to music frequently, but it may not be as attractive to heavy users.
Impact of Pricing
- User acquisition:Lower prices can attract new users, but they may also limit revenue potential.
- User retention:Value-added services and exclusive content can increase user satisfaction and reduce churn.
- Revenue generation:A balance must be struck between maximizing revenue and maintaining user affordability.
Value-Added Services
Music websites offer value-added services to enhance user experience, increase revenue, and differentiate themselves from competitors:
Personalized Playlists
Customized playlists based on user listening history and preferences provide a tailored and engaging music experience.
Exclusive Content
Original podcasts, interviews, and behind-the-scenes footage offer exclusive content that attracts and retains users.
Artist Merchandise
Partnerships with artists allow music websites to sell exclusive merchandise, providing additional revenue streams and fan engagement opportunities.
Return on Investment
Value-added services can generate revenue through direct sales, subscriptions, and increased user engagement. They also contribute to user satisfaction and loyalty, which can lead to reduced churn and increased overall revenue.
Market Segmentation
Music websites target different market segments based on demographics, music preferences, and spending habits:
Demographics
- Age
- Gender
- Income
- Location
Music Preferences
- Genres
- Artists
- Listening habits
- Music discovery methods
Spending Habits
- Subscription willingness
- Budget for music
- Frequency of music purchases
- Value-added services interest
Tailored Marketing Campaigns
Understanding market segments allows music websites to develop targeted marketing campaigns that effectively reach and engage each segment.
Competitive Landscape
The music website industry is highly competitive, with several key players:
SWOT Analysis
| Competitor | Strengths | Weaknesses | Opportunities | Threats |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spotify | – Large user base
|
– High subscription costs
|
– Expansion into new markets
|
– Competition from other streaming services
|
| Apple Music | – Integration with Apple ecosystem
|
– Smaller music library than Spotify
|
– Expansion into new markets
|
– Competition from other streaming services
|
| Amazon Music Unlimited | – Integration with Amazon Prime ecosystem
|
– Smaller user base than Spotify and Apple Music
|
– Expansion into new markets
|
– Competition from other streaming services
|
Differentiation
Music websites can differentiate themselves by:
- Exclusive content and partnerships
- Personalized recommendations and user experience
- Value-added services and community features
- Targeting specific market segments
Revenue Optimization: A Music Website Charges X Dollars
Music websites generate revenue through multiple streams:
Advertising
Display ads, sponsored content, and audio ads provide revenue from advertisers.
Subscriptions
Recurring revenue from subscription fees is a key revenue source for many music websites.
Other Sources
- Value-added services (e.g., artist merchandise, exclusive content)
- Data licensing and partnerships
- Event ticketing and merchandise sales
Data Analytics
Data analytics play a crucial role in revenue optimization by identifying:
- User behavior and preferences
- Effective marketing campaigns
- Opportunities for cross-selling and upselling
FAQ Corner
What factors should a music website consider when determining its pricing strategy?
Factors to consider include target market, competition, value-added services, and revenue goals.
What are the advantages of a flat-rate pricing model?
Simplicity, ease of understanding, and predictability of revenue.
How can a music website differentiate itself from competitors in terms of pricing?
By offering unique value-added services, targeting specific market segments, and leveraging data analytics to optimize pricing.

